Your retina is a vital part of your eye that plays a crucial role in how you see the world. Located at the back of your eye, this thin layer of tissue captures light and sends signals to your brain, allowing you to process images. Because the retina is so important to vision, any damage or disease affecting it can lead to serious sight problems. The good news? A comprehensive eye exam can detect retinal issues early—sometimes before you even notice symptoms.
At Pacific Eye Institute, our team of specialists, including Dr. Daniel D. Esmaili, Dr. Chang Sup Lee, Dr. Samuel C. Kim, and Dr. Douglas R. Matsunaga, are experts in diagnosing and treating retinal conditions. Let’s explore some of the most common retinal diseases and what an eye exam can reveal about your eye health.
Common Retinal Conditions an Eye Exam Can Detect
1. Retinal Detachment or Tears
One of the most serious retinal conditions is retinal detachment, which occurs when the retina pulls away from the back of the eye. This can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated promptly. Warning signs include:
- Sudden flashes of light
- An increase in floaters (tiny spots or lines in your vision)
- A shadow or curtain appearing over your vision
During an eye exam, your doctor will check for any lifting, tearing, or detachment of the retina and recommend immediate treatment if necessary.
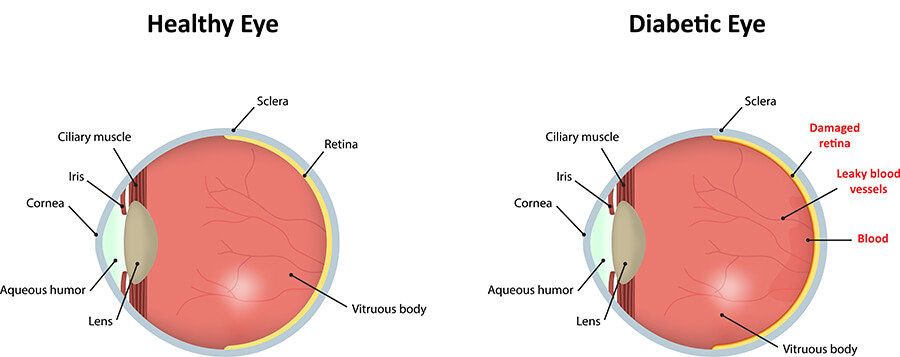
2. Diabetic Retinopathy
People with diabetes are at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy, a condition where high blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina. This can lead to:
- Blurry vision
- Spots or floaters
- Dark areas in vision
If left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can cause severe vision loss. Routine eye exams allow early detection and management to prevent complications.
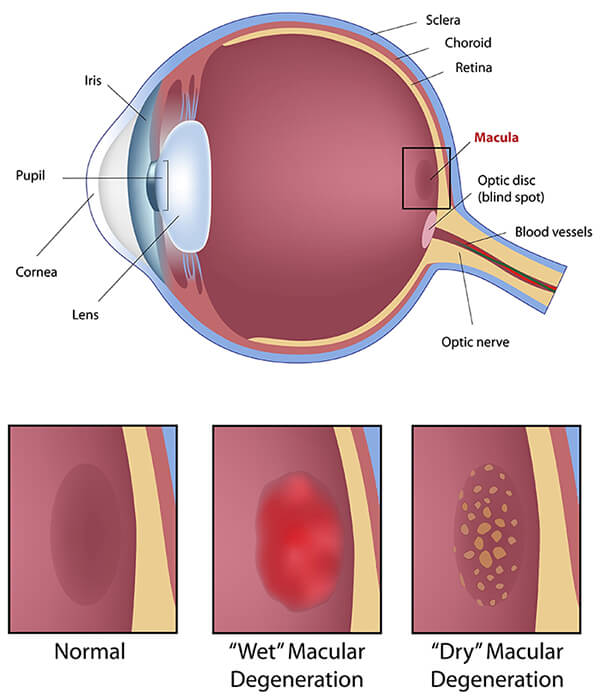
3. Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
AMD is a common condition that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. Symptoms include:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Difficulty reading or recognizing faces
- Dark spots in central vision
An eye doctor can identify AMD by looking for yellow deposits (drusen) or signs of bleeding in the retina. Early intervention can help slow its progression.
3. Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
AMD is a common condition that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. Symptoms include:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Difficulty reading or recognizing faces
- Dark spots in central vision
An eye doctor can identify AMD by looking for yellow deposits (drusen) or signs of bleeding in the retina. Early intervention can help slow its progression.
4. Retinal Vascular Occlusions
A blockage in the veins or arteries of the retina can cause sudden vision loss. This happens when blood flow to the retina is restricted, leading to swelling and hemorrhages. An eye exam can detect these signs and determine if underlying health issues, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, may be contributing factors.
5. Hypertensive Retinopathy
High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to hypertensive retinopathy. This condition often has no symptoms at first, but an eye doctor may notice:
- Narrowed or swollen blood vessels
- Bleeding in the retina
- Fluid buildup
Managing blood pressure and regular eye checkups can help protect your vision from long-term damage.
6. Retinitis Pigmentosa
This inherited condition affects peripheral vision and night vision. Over time, it can lead to tunnel vision and even complete blindness. Signs your eye doctor may find include:
- Dark pigment deposits in the retina
- Thinning of retinal blood vessels
While there is no cure, early detection can help manage symptoms and slow progression.
7. Macular Hole or Epiretinal Membrane
These conditions affect the macula and can cause blurry or distorted central vision. A macular hole is a small break in the macula, while an epiretinal membrane is a layer of scar tissue that can wrinkle the retina. Symptoms include:
- Difficulty seeing fine details
- Straight lines appearing wavy
- A gray or blurry spot in vision
An eye exam can help identify these conditions early, allowing for timely treatment options such as surgery.
How Are Retinal Conditions Detected?
A comprehensive eye exam involves several tests to assess the health of your retina. Your doctor may use one or more of the following:
- Dilated Eye Exam – Your pupils are dilated with special eye drops so the doctor can examine the retina and optic nerve in detail.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) – This imaging technique provides cross-sectional images of the retina, helping to detect abnormalities.
- Retinal Photography – High-resolution images of the retina allow for close examination and comparison over time.
- Fluorescein Angiography – A dye is injected into your bloodstream to highlight blood flow in the retina, revealing blocked or leaking blood vessels.
- Ultrasound – This is useful for cases where the retina is obscured due to bleeding or cloudiness.
Why Early Detection Matters
Retinal diseases can develop silently, without noticeable symptoms in the early stages. By the time vision loss occurs, the damage may already be significant. That’s why routine eye exams are essential, especially if you have risk factors such as:
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- A family history of eye disease
- Aging (certain conditions become more common as you get older)
Early diagnosis can lead to timely treatments that protect your vision and improve outcomes.
At Pacific Eye Institute, we are committed to providing the highest level of eye care. If you haven’t had an eye exam in a while, or if you’re experiencing any changes in your vision, don’t wait. Call us (800) 345-8979 to schedule an appointment with us today and take the first step in protecting your sight.
Your vision is priceless, let us help you preserve it.








